

SEO has become increasingly challenging, and even mystifying lately. The rules of the game change so quickly, it can be hard to keep up.
As algorithms are updated so frequently, it’s hard to know for certain whether your strategy is performing well, how it stacks up to your competitors, and whether you’re behind the curve with current trends.
There’s a solution.
Industry benchmarks are the key of successful SEO, and it’s crucial to understand them to set realistic expectations and gauge your results.
This Rundown is based around this idea: how to use data and benchmarks to craft a strategy that’s effective, and removes the guesswork from your process.
If you’re struggling with unclear SEO performance, a lack of competitive insights, and challenges in adapting strategies to shifting trends, you’ll find something helpful here.
You’ll especially find “Benchmarking in Action: Practical SEO Tips for Business Success” useful, and you’ll see how benchmarking can transform your SEO strategy with data-driven insights and practical tips to boost your organic search performance and growth.
Time to start analyzing and creating a strategy that works.

Katie Morton Editor in Chief, Search Engine Journal
Benchmarking in Action: Practical SEO Tips for Business Success
Discover how benchmarking can transform your SEO strategy with data-driven insights, practical tips, and industry-specific benchmarks to help boost your organic search performance and growth.
 Conductor
7.7K Reads
Conductor
7.7K Reads

Businesses are constantly vying for organic search traffic to maintain a competitive edge. One powerful way to enhance SEO efforts is through benchmarking.
By comparing your SEO performance against industry-specific benchmarks, you can gain valuable insights into your current brand standing within the market, evaluate your SEO strategy, and identify key areas for growth and opportunities.
Many businesses face uncertainty when it comes to evaluating their SEO efforts. Without clear performance indicators, they struggle with a lack of competitive insights and face challenges in adapting strategies effectively.
Benchmarking addresses these pain points by offering concrete, data-driven insights, enabling you to refine your strategies, boost visibility, and ultimately maximize your organic traffic.
This article explores how benchmarking can empower you and your business to make data-driven decisions that drive better organic search results and sustainable growth.
Vital Benchmarks For SEO Success
When it comes to SEO, different benchmarks provide valuable insights that can help you refine your strategies and improve performance. Monitoring these benchmarks gives you a clear view of your brand’s competitive standing, opportunities for quick wins, and areas for growth.
A few benchmarks you’ll find beneficial include:
- Organic traffic & impressions
- Rankings
- Rich search result feature performance
- Share of voice
- Clicks and conversions
- Bounce rates and engagement
- Backlinks and referrers
Where do you find industry SEO benchmarks?
Get a copy of our 2024 Organic Search Traffic Benchmarks Report. Inside, you’ll find a wealth of industry-specific insights and statistics, including:
- Search traffic statistics
- Rich search result benchmarks
- Content insights
- Data exploring the impact of AI overviews on industry SERPs
Curious about what you can do with these kinds of statistics?
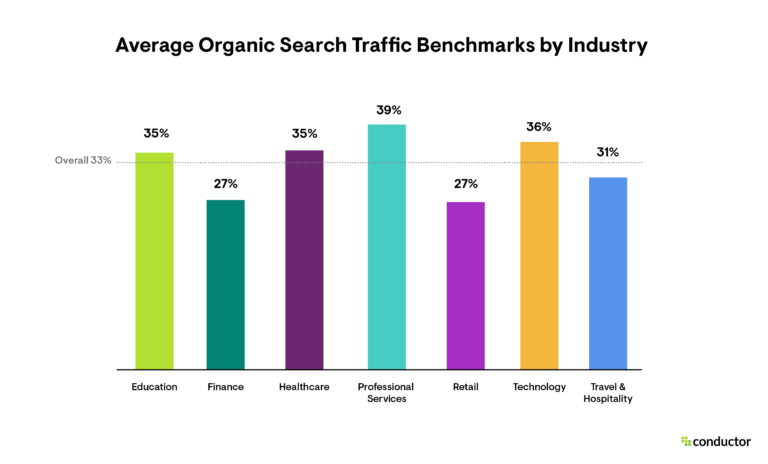 Image from Conductor, October 2024
Image from Conductor, October 2024
Industry-Specific Benchmarks Help Set Realistic Expectations
Each industry has unique challenges, customer behaviors, and competitive landscapes. For example, organic search performance in healthcare differs significantly from that in retail or finance. By analyzing industry-specific benchmarks, businesses can set realistic SEO goals and expectations tailored to their market’s dynamics.
For instance, in our 2024 Organic Search Traffic Benchmarks Report, businesses in the retail or finance sectors can expect to receive only 27% of their traffic from organic search. In contrast, brands in the technology, education, or professional services industries typically receive 35% or more of their traffic from organic search.
Knowing these industry averages helps you set achievable goals and prevents you from chasing unrealistic targets.
Benchmarking, KPIs, And Tracking Success
It would be unfair and unproductive to measure the success of an e-commerce company using the same metrics as a professional services website. That’s where industry-specific data comes in.
Benchmarking plays a crucial role in setting the right KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) for SEO strategies and campaigns. By analyzing industry-specific benchmarks, you can establish realistic, data-driven KPIs that align with your market conditions and competitive landscape.
This approach ensures that your SEO goals are both measurable and achievable, while providing a clear method for evaluating success.
For example, a business in the healthcare industry might focus on metrics like page load speed and mobile optimization, while an e-commerce company would likely prioritize conversion rates and organic search traffic data.
Performance Insights And Identifying Growth Opportunities
Benchmarking provides you with a comprehensive view of your current SEO performance, allowing you to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for growth. By comparing key metrics like organic traffic, bounce rates, and conversion rates against industry averages, you can more accurately pinpoint underperforming areas and focus your efforts on improvement.
For instance, if your organic traffic is below the industry average, it might indicate a need for better content optimization, stronger keyword strategies, or improvements in technical SEO. Armed with these insights, you can implement targeted strategies to close performance gaps and achieve more competitive results.
Branded Vs Non-Branded Traffic Benchmarks
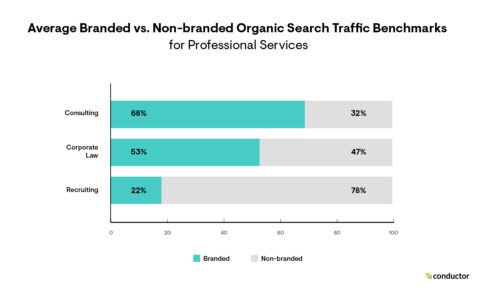 Image by Conductor, October 2024
Image by Conductor, October 2024
Understanding the balance between branded and non-branded traffic is another critical aspect of benchmarking. This data enables you to assess how effectively you’re capturing general market interest and positioning yourself as a leader in your niche.
If your business heavily relies on branded traffic, it may signal strong brand recognition, but it could also indicate a missed opportunity for broader keyword optimization. On the other hand, a high volume of non-branded traffic might suggest you are successfully capturing new customers, but you may need to strengthen your brand’s presence.
Striking the right balance for your specific market matters, too. For example, in our 2024 Search Traffic Benchmarks Report, we found consulting services receive far more branded traffic (68%) than recruiting services (22%). These numbers reflect the importance of brand when searching for respective services, as well as the prominence branding holds in users’ minds when performing a search.
By analyzing this data, you can fine-tune your SEO strategies to capitalize on both branded and non-branded opportunities.
Benchmarks For Rich Search Result Optimization
 Image from Conductor, October 2024
Image from Conductor, October 2024
Featured snippets, People Also Ask sections, and other rich search results are becoming increasingly important for visibility and driving traffic. Benchmarking can help you evaluate how well your site performs in these rich SERP features compared to your competitors.
It can also help you determine which rich search features are worth investing time in, and which pages to focus on.
For example, if a competitor consistently ranks in featured snippets while your business does not, this could indicate an opportunity for optimization. Adjusting content to target long-tail keywords, answering common questions, and structuring content with clear headings and bullet points can increase the likelihood of appearing in these rich results.
Our report also finds that video-rich search results currently appear only 14% of the time, but this number is growing steadily, indicating that users increasingly prefer hearing directly from legal experts through video rather than reading optimized, text-based content.
As a result, creating clear, informative videos featuring various lawyers can improve organic search visibility, humanize your services, and foster trust with potential clients.
Benchmarking for Improved Performance
Page performance can benefit from benchmarking as well. For example, if your industry typically receives higher mobile traffic, you can use benchmarking to measure your site’s performance and ensure it is fully optimized for mobile users to improve user experience and rankings.
In addition to mobile optimization, benchmarking can highlight areas where technical SEO improvements are needed, such as site speed, URL structure, and overall site health. Comparing your website’s load times and technical performance against industry standards allows you to identify weaknesses that may be impacting user experience or search rankings.
Content Insights and Benchmarking
Regularly evaluating content performance helps maintain high-quality standards and relevance over time. Benchmarking can reveal content gaps, providing a roadmap for creating more relevant and comprehensive articles.
You can use benchmark data to adapt to changing industry trends and audience preferences, staying ahead of emerging topics and ensuring your content remains fresh and competitive.
With Conductor’s content provider benchmarks, you can see which brands dominate the content in your industry-relevant SERPs. Additionally, it provides insights into how to overcome their seemingly unshakable strategies and win, driving more organic traffic to your brand.
Taking Action with Benchmarking
Benchmarking serves as a valuable tool for businesses across industries, offering a data-driven approach to improving SEO strategies and setting realistic goals.
By leveraging industry-specific data, optimizing for rich search results, and analyzing branded versus non-branded traffic, you can secure a competitive edge in your market and boost organic search performance.
As you evaluate your SEO performance, consider how Conductor can help you achieve your goals. Our platform offers in-depth performance insights, comparative industry data, and practical recommendations to drive meaningful results.

12 Essential Steps In Building A Winning SEO Strategy
Laying a solid foundation will help your SEO strategy pay off for years to come. Don't miss these fundamental first steps.
 Loren Baker
41K Reads
Loren Baker
41K Reads

SEO is not just about optimizing for search engine rankings. It’s also about understanding your audience’s needs and providing solutions through your website or landing page.
Google alone processes over 100 billion searches a month. So, if you get your strategy right, the potential to reach new customers through search is immense.
But here’s the catch: Search algorithms are always changing. The recent introduction of generative AI directly in search has shaken up how users interact with search engines.
What that means for SEO is that you can’t just set it and forget it – your SEO strategy needs to adapt to these changes to stay competitive.
You need to regularly analyze and course-correct to ensure you’re taking advantage of the latest best practices and strategies.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps for creating an effective SEO strategy that aligns with both search engine algorithms and user expectations.
1. Align SEO With Business Goals & Define KPIs
It’s crucial to align your SEO strategy with your overall business goals and define the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will help you measure success.
Knowing where you want to go and how you’ll measure progress ensures that your SEO efforts are focused and effective.
Your SEO goals should support your business objectives, whether that’s increasing brand awareness, driving more traffic, generating leads, or boosting sales.
During this planning phase, you’ll want to define your KPIs.
This is how you’ll measure the success of your implementations and figure out what’s working for you and where you need to make adjustments.
Some of the SEO KPIs you should be tracking are:
- Visibility in search (segmented by search features such as AI Overviews, featured snippets, Local Packs, etc.).
- Traffic from search (organic traffic).
- Keyword rankings.
- Branded searches.
- Quality backlinks.
- New and returning users.
- Leads and conversions.
- ROI from organic channel.
- Pages per session.
- Average engagement time on page and bounce rate. (Bounce rate is not a universal metric for everyone, but is 100% dependent upon the events you set up).
- Core Web Vitals.
- Crawl errors.
Keep in mind that these are internal SEO KPIs that you can track in analytics.
Higher-level executives may be more interested in overall business impact, such as SEO-supported attribution and how SEO contributes to the customer journey.
It’s also important to convey that SEO is a long-term strategy that may take time to show significant results.
2. Set Realistic Expectations
One of the most common mistakes people unfamiliar with SEO make is expecting overnight results.
SEO is not a direct response style of marketing, and not all SEO strategies result in an immediate outcome.
Because of the variables involved with competition, inbound links, and the content itself, it’s nearly impossible to provide a definite timeframe.
You need to go into the process with an understanding that SEO takes time, and the more competitive the keywords you’re going after, the longer it will take to climb to the top.
This needs to be conveyed to stakeholders from the start to ensure expectations are realistic and to establish consistent, accurate data that earns trust.
SEO can be part of the entire customer journey.
Someone might find your site via organic search, then later see a paid ad, and finally make a purchase. Or they might see an ad first, then search for your brand and find you organically.
This is where multi-touch attribution comes into play. Using multi-touch attribution tracking tools like Triple Whale can help you understand how different channels contribute to conversions.
3. Conduct SEO Audit
Now that you’ve aligned your SEO strategy with your business goals and set the right expectations, it’s time to understand where you currently stand.
You’ll want to begin by performing an SEO audit.
An SEO audit serves as the roadmap that will guide you throughout the entire optimization process and allows you to benchmark against your current site.
You need to examine a variety of aspects, including:
- Domain name, age, history, etc.
- On-page SEO factors like headlines, keyword & topical targeting, and user engagement.
- Content organization, content quality, and the quality of your images (no one trusts stock photography).
- Duplicate content.
- Backlink profile quality.
- Website architecture.
- Technical SEO factors like sitemaps, image optimization, and robots.txt.
- Implementation of hreflang tags for multilingual sites.
For a step-by-step guide on how to perform this audit, we have an excellent series that will guide you through it.
Once you have a clear understanding of your current SEO status, it’s time to plan your timeframe and allocate budgets and resources.
This is yet another area of life where you get what you pay for. If you’re looking for fast and cheap, you’re not going to get the results you would by investing more time and money.
Obviously, your budget and timeframe will depend on your company’s unique situation, but if you want good results, be prepared to invest accordingly.
For an idea of how much you should be spending, consult this article.
4. Perform Keyword Research
Search engine rankings are determined by an algorithm that evaluates a variety of factors to decide how well a website answers a particular search query. And a huge part of that is the use of keywords.
From single words to complex phrases, keywords tell search engines what your content is about. But adding keywords isn’t quite as simple as just plugging in the name of the product or service you want to sell.
You need to do research to ensure keyword optimization and avoid cannibalization, and that means considering the following:
Search Intent
Words often have multiple meanings, which makes it crucial to consider search intent, so you don’t attract an audience that was searching for something else.
For example, if you sell hats, ranking highly for ‘bowler’ will attract users looking for 10-pin bowling in the U.S., or in the UK about cricket and not someone shopping for a bowler hat.
Relevant Keywords
Once you’ve identified the search intent of your target audience, you can determine which keywords are relevant to them.
By aligning your keywords with search intent, you can produce relevant content and increase your chances of ranking higher in SERPs. Besides ranking high, it will also improve user satisfaction and increase conversion rate.
Keyword Research Tools
The brainstorming process is a great place to start keyword research, but to ensure you’re attracting the right audience and proving your value to search engines, you should utilize a research tool.
They can provide valuable data, such as search volume and competition level, and suggest related keywords you might not have considered.
Search Volume
By using keyword research tools, one of the most important metrics to look for is the search volume.
Ideally, you should target relevant keywords with the highest search volumes. However, it is important to assess the competition around that search term.
If you are going to compete with large and well-established brands and you are just starting, perhaps it is a better idea to choose long-tail keywords with less search volume but less competition.
Long-Tail Keywords
These are specific search terms consisting of more than one word.
They tend to be longer and are more likely to be used by people with specific stages in the conversion funnel, helping you reach users who are ready to convert.
An example of this would be [vegetarian restaurants in San Antonio], which would most likely be used by someone with a craving for a plant-based meal.
Lastly, remember that tools provide aggregate data of the same search terms with measurable search volumes, which they obtain from different data providers.
Often, there are long-tail searches that users perform, which are the same but formulated differently, and tools may report them as zero search volume due to negligible search volumes.
This phenomenon is likely to increase as highly intelligent AI assistants are integrated into mobile phones, and users are more likely to perform unique voice searches on the same issue.
If a certain problem is relevant to your specific industry and you know it, but tools report zero search volume, it is worth covering it and offering a solution.
You may find you have decent and highly targeted traffic that converts.
5. Define Your Most Valuable Pages
Every team needs an MVP, and in the case of your website, that’s your most valuable pages.
These pages are the ones that do the bulk of the heavy lifting for you.
For non-ecommerce sites, these are usually things like your home page, your services pages, or any pages with demos or other offers.
These pages are also likely MVPs for ecommerce sites, but will also be joined by category and/or product-level pages.
To find which pages are your site’s most important ones, you should consider what your organization is known for.
What verticals do you compete in? What pain points do you solve? Define these or add more based on the high-level keywords you came up with in the previous step.
Once you’ve identified the category and product pages that bring in the most visitors, you’ll be able to focus your strategy on improving them and increasing your organic traffic.
Read more about how to find your MVPs here.
6. Keep Content Up To Date
Your MVP pages become stale over time while search engines aim to surface for users the most relevant and up-to-date content.
Content decay is a natural process; you should set up a process to keep content up to date constantly.
Here is an example from one of the websites I work on, showing how it looks and highlighting the importance of updating outdated content.
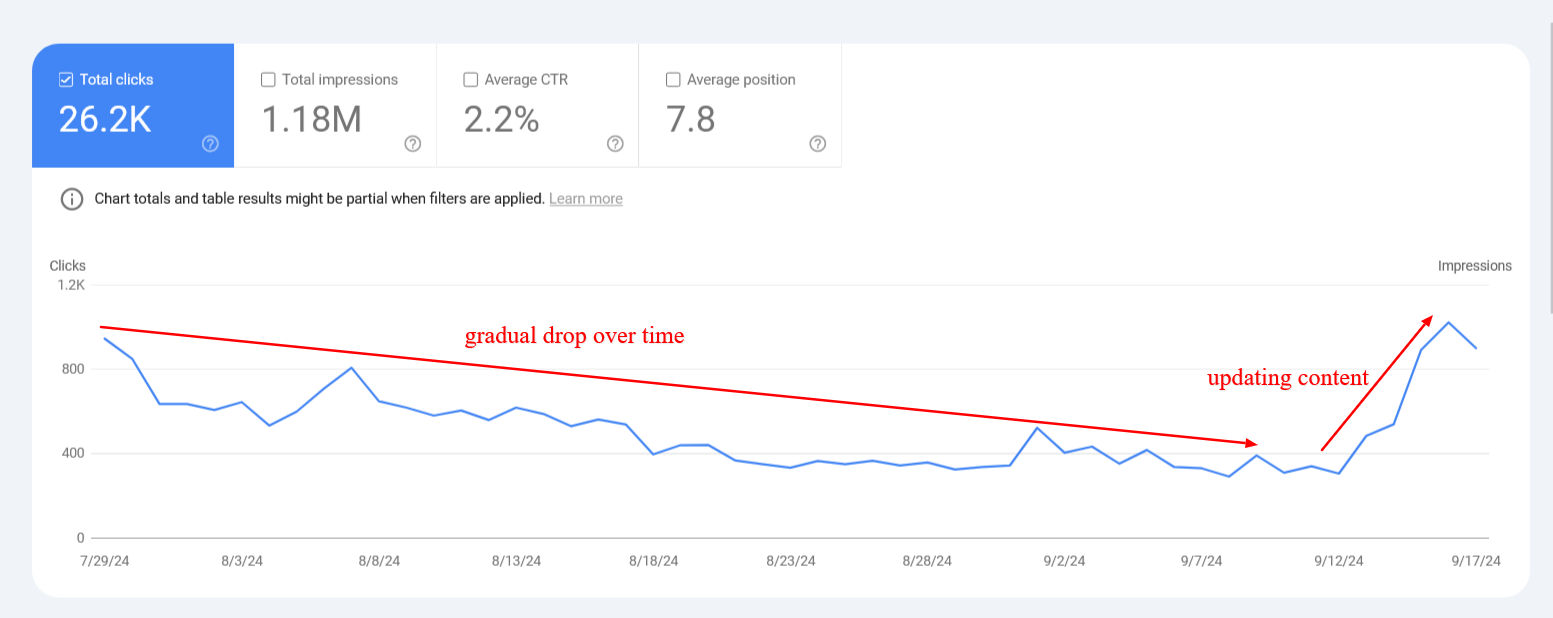 An example of content decay: updating content helped regain organic traffic.
An example of content decay: updating content helped regain organic traffic.
Please note that you should refrain from using automatic updates with AI chatbots, as it is one of the most dangerous, spammy SEO tactics that can result in a complete loss of organic traffic.
Read our guide to learn content decay strategies you can implement to keep your organic traffic growing.
7. Optimize For User Experience
Don’t overlook the importance of how your site is structured, both technically and in terms of how users interface with it.
The best content and keyword strategy in the world won’t lead to a single sale if your site is constantly broken or is so frustrating to use that people close your page in disappointment.
You should carefully consider your site’s architecture and user experiences to ensure people are taking the desired actions.
With mobile traffic being 62.15% of total web traffic (and 77% of retail website traffic), optimizing for mobile is even more critical.
Read our guide UX & SEO Guide to learn more.
8. Conduct A Competitive Analysis
If you didn’t have any competition, there would be no need for SEO. But as long as other companies are manufacturing refrigerators, Frigidaire needs to find ways to differentiate itself.
You need to have an idea of what others in your industry are doing so you can position yourself for the best results.
You need to figure out where you’re being outranked and find ways to turn the tables.
You should know which keywords are most competitive and where you have opportunities by performing content gap analysis.
You should understand your competitor’s backlinking and site structure so that you can optimize your own site for the best possible search ranking.
And remember, AI chatbots are your competitor, too, where users can get answers directly without visiting a website.
This means that some of the traffic you might have received in the past could now be staying in the chatbot.
To compete, you need to offer something AI can’t: unique insights, personal experiences, and authoritative content that stands out.
Consider how AI presents information and find ways to differentiate your content. Focus on building your brand authority and providing value that AI chatbots can’t replicate.
Learn more about how to perform this analysis and develop a template for it by reading this piece.
9. Establishing Brand Authority And Link Building
All the points we covered so far are essential for success in SEO, but they are not enough.
You can achieve success by merely improving your website, and if you aim for your brand to exist only in Google Search, you will likely not be able to rank and achieve success.
That is why you need to work on your brand marketing tirelessly in order to build your brand authority, which, in turn, helps you earn natural backlinks as a recognized and trustworthy source.
It’s not such an easy thing to get right, and that is where most companies struggle and why SEO is hard.
To build brand authority, you need the following steps:
- Build an email newsletter list.
- Share valuable research and insights others want to link to.
- Attend conferences relevant to your field and sponsor them if you have enough resources.
- Seek opportunities for interviews or speak at conferences.
- Host webinars or live sessions to share knowledge and interact with your audience in real time.
- Participate in online discussions with your industry community on different platforms such as Linkedin, Twitter, Reddit, or other platforms specific to your industry.
- Collaborate with experts in your industry to contribute to your content.
- Invite influencers to try your products or services and share their experiences.
- Offer effective support to your customers.
Even if you get unlinked brand mentions, it is a step forward in building brand awareness.
Think of for a moment if one reads your unlinked brand mention on a reputable website (or on a TV show) and performs a Google search to find your brand.
That could be considered as a branded search which is a ranking factor. It is important to note unlinked mentions are not a ranking factor as there is much misinformation out there, but when one performs a branded search on Google.
Of course, you can go ahead and try to convert an unlinked mention to a link, and it is always one of the natural ways to build a link.
However, in the age of AI, another benefit of unlinked brand mentions is that chatbots – which are trained on content across the web – may surface your brand name to users when they perform tasks or research.
10. Integrate SEO Into Your Workflows
SEO doesn’t exist in a vacuum – it impacts many other parts of your organization, including marketing, sales, and IT.
If you’re looking for the budget to perform SEO, you may find some of your employees are already well-qualified to help.
For example, your sales team probably knows which products people are most interested in.
Enlisting them in your SEO strategy development will help with lead generation and finding new targets who are already qualified.
Similarly, SEO can tell your marketing team what types of content resonate best, so they can fine-tune their campaigns. And your copywriters and graphic designers can develop the type of content that will help you shoot up the rankings.
Your IT team probably already has control over your website.
Your SEO strategy should be designed around their expertise, to ensure website design and structure, development cycles, data structure, and core principles are all aligned.
Evaluate your existing software, technology, and personnel, as there’s a good chance you have some of the pieces already in place.
If you need to scale production up, you may find the budget already in place in existing departments.
These are just a few ways to integrate SEO into your existing workflows.
If you’re an external SEO agency or consultant, it’s crucial to establish strong communication channels with the company’s personnel who are responsible for implementing SEO recommendations and making decisions.
Read our guide on best practices for establishing effective communication between SEO teams in enterprise companies.
11. Align Your SEO Strategy With Your Customer Funnel
At the end of the day, sales are the name of the game. Without customers, there’s no revenue, and that means no business.
To aid in the sales process, your SEO strategy should align with your customer funnel.
Sometimes described as the customer journey, your sales funnel is a summation of the touchpoints customers have with your company as they go from awareness to post-purchase.
SEO fits neatly with every stage of this cycle:
- Awareness: In the modern world, many customers first hear about your business online through a Google search, for example. Well-written blog posts are a great way to increase your awareness and increase your brand recognition.
- Interest: This is where customers start doing research. And what better place to do research than your website? In-depth guides and ebooks will be a great match for satisfying users’ interests.
- Decision: The customer wants to buy and is deciding between you and the competition. Case studies or testimonials could be the thing that sways them.
- Purchase: Having a search engine-optimized point of sale makes it easy for people to buy, and optimized product pages are what can move the needle.
- Post-purchase: Once you’ve acquired customers, think of ways to retain them by publishing support articles or offering loyalty programs.
12. Report And Measure
Finally, you need to define what success looks like for each KPI measure and report the progress you’re making.
There are a variety of both paid and free tools available that you can use to measure and track conversions, and compare them weekly, monthly, or by another timeframe of your choosing.
Simply find one that works for your budget and needs.
For a guide on how to create impactful reports that generate quality insights, read our guide here.
Conclusion
No one ever said SEO was easy, at least not anyone who has done it. But it’s a vital part of any modern organization’s business plan.
However, with a solid strategy, a willingness to learn, and a little old-fashioned elbow grease, even a complete beginner can send their website to the top of the SERP.
In this piece, we’ve given you 12 steps to take to get your SEO strategy off the ground. But of course, this is just the start.
You need a unique plan that will work for your industry and your needs.
Luckily, Search Engine Journal can help with this, too.
Download our ebook on SEO strategy with a full-year blueprint for an easy-to-follow 12-month plan you can use to develop a solid strategy, track your progress, and adjust to changing situations.
More resources:
- 7 Strategic SEO Insights & Tactical Tips For 2024 And Beyond
- The Importance Of Starting Your SEO Campaign With Strategy Development
- SEO Strategy: A Full Year Blueprint (+Template) [Ebook]
Featured Image: Ingenious buddy/Shutterstock
Making SEO Decisions With Confidence: A Guide To Data-Driven Strategies
Data is the new gold. Learn how to use data for a customer-centric SEO strategy to increase traffic and revenue for your business.
![]() Adam Heitzman
5.4K Reads
Adam Heitzman
5.4K Reads

In SEO, making strategic decisions without empirical data is like relying on luck for consistent results.
But how can you effectively harness data to guide your SEO efforts and ensure you’re not just shooting in the dark?
This comprehensive guide will show you how to leverage data for confident, results-driven SEO strategies.
The Power Of Data-Driven SEO: A Case Study
Let’s start with a compelling example. Glassdoor.com, before its sale to Recruit Holdings in 2018, had an impressive 29,500,000 in monthly traffic – almost entirely organic.
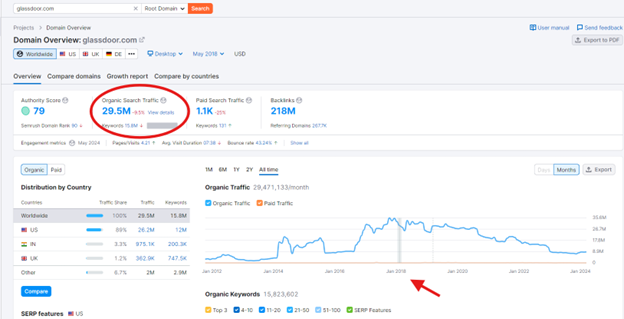 Screenshot from Semrush, September 2024
Screenshot from Semrush, September 2024
Their success wasn’t by chance; it was the result of a meticulous, data-driven approach to SEO.
In her 2017 presentation at a marketing summit, Dawn Lyon, vice president of corporate affairs, shared how they weaved data from different internet sources.
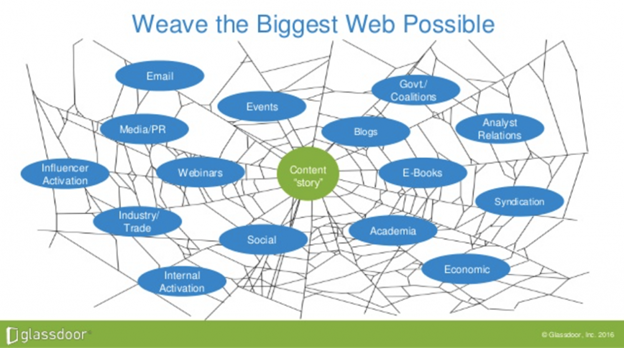 Image from Dawn Lyon/Glassdoor, September 2024
Image from Dawn Lyon/Glassdoor, September 2024
Glassdoor’s strategy involved analyzing data from various internet sources to identify content gaps and create high-value, well-optimized content.
This approach led to over 200,000,000 backlinks from more than 200,000 websites, establishing their influence and authority in the online employment industry.
The takeaway? Glassdoor used data to identify valuable content assets and gaps, creating content that brought them closer to their prospects.
This data-driven strategy significantly influenced their rankings in search results for the online employment industry.
What Types Of Data Are Important In SEO?
Before diving into strategies, it’s crucial to understand the types of data that matter in SEO:
- Traffic data: This includes organic traffic, direct traffic, referral traffic, and paid traffic. It helps you understand how users are finding your site.
- Keyword research data: This reveals the terms and phrases people use to find websites like yours. It’s crucial for content planning and on-page optimization.
- Backlink data: These are links from other websites to yours. Search engines consider them a sign of trust and authority.
- Competitor data: This shows competitor performance and strategies, helping you identify opportunities and threats in your niche.
- Content data: This includes information about your website’s content, such as word count, readability score, and internal linking structure.
- User behavior data: Metrics like bounce rate and session duration offer insights into user experience and content effectiveness.
- Technical SEO data: This gives information on website performance, such as page load speed and mobile-friendliness.
- Conversion rate data: Based on your desired outcomes, conversion rate tells you where you need to improve and how you can optimize for better results.
Each of these data types provides unique insights that can inform your SEO strategy.
The Importance Of Data In SEO
Data takes the guesswork out of SEO, allowing you to focus on what works based on empirical evidence. For instance:
- Keyword research data helps you understand your target audience’s pain points.
- Bounce rate data can help you address issues affecting user engagement.
- Engagement metrics show which content resonates with your audience.
How To Use Data In Your SEO Strategy
Now, let’s explore how to implement data-driven strategies in your SEO efforts:
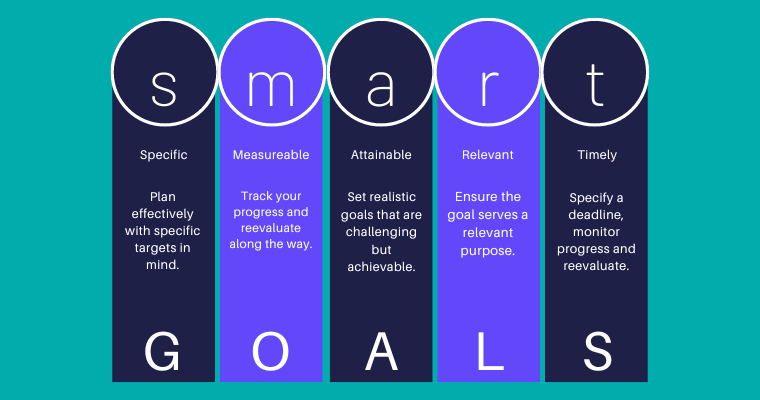
1. Define Clear Objectives For SEO
Start by setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) SEO objectives. This helps you navigate the volume of available data and prioritize key areas for your campaigns.
 Screenshot taken by author, September 2024
Screenshot taken by author, September 2024
2. Establish Baseline Metrics And KPIs
Identify KPIs that align with your objectives and establish baseline metrics to measure current performance. This provides a reference point for evaluating the impact of your SEO strategy.
 Screenshot from Semrush, September 2024
Screenshot from Semrush, September 2024
3. Understand User Intent
Analyze search intent behind keywords to effectively optimize your content. Use tools like Google Search Console to track click-through rates (CTR) for individual pages, which can indicate how well your content matches user intent.
4. Choose High-Opportunity Keywords
Identify “low-hanging fruit” keywords with significant search volume and low to moderate competition. Evaluate their business potential before targeting them.
 Screenshot from Ahrefs, September 2024
Screenshot from Ahrefs, September 2024
5. Gather And Analyze Your Website Data
Use tools like Google Analytics to track your website traffic and user engagement metrics. This data can provide insights into your search performance and help you identify areas for improvement.
6. Conduct Competitor Analysis
Identify your SEO competitors and analyze their strategies. Tools like Semrush can help you find keyword gaps and backlink opportunities.
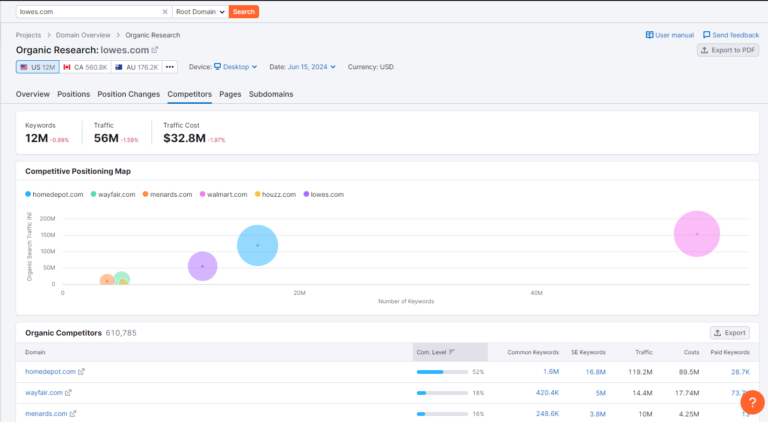 Screenshot from Semrush, September 2024
Screenshot from Semrush, September 2024
7. Create A Data-Driven SEO Strategy
Based on your gathered data, create an informed SEO strategy. This should include:
- Creating your ideal customer profile.
- Targeting the right keywords.
- Conducting a site-wide audit.
- Creating a content calendar.
8. Double-Down On High-Performing Keyword Categories
Identify which keywords drive the most organic traffic and conversions on your site. Use Google Search Console to see which terms rank highest and attract the most click-throughs from search results.
If you use a rank-tracking tool, combine this data with Google Analytics to see how pages perform in terms of traffic, engagement, and conversions.
Once you’ve identified your best-performing keywords, expand your content footprint within these high-value areas.
For example, if “beginner yoga poses” is a top performer, consider developing content for related terms like “yoga poses for flexibility,” “yoga routines for beginners,” and “best yoga mats for beginners.”
These “content clusters” around a topic will help you capture more traffic from thematically related keywords and can increase your domain’s overall authority for that topic area.
9. Analyze What Makes Your Best Content Effective
Examine your highest-performing content to identify factors that make it engaging for users. Consider aspects like:
- Word count: Is longer content performing better, or do users prefer concise information?
- Tone of voice: Is a casual, conversational tone more effective, or do users respond better to a formal, authoritative voice?
- Presentation: How does the use of headings, bullet points, images, and other visual elements impact engagement?
- Originality: Are unique insights or original research driving more engagement?
- Expertise demonstrated: How does the level of experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) impact performance?
- Call-to-action (CTA): Analyze the clarity and appeal of your CTAs. Are they driving the desired user actions?
Understanding which of these variables plays a part will guide you in crafting future content that might mirror the same success.
10. Eliminate Friction From Your Conversion Paths
Analyze which user journeys lead to the highest levels of conversions. Look for commonalities in these high-converting paths and aim to replicate these elements across your site.
11. Prioritize Core Web Vitals
Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to evaluate your site’s performance across Core Web Vitals metrics. Implement recommended fixes to improve your site’s user experience.
12. Enhance Your Site’s Mobile Usability
With mobile accounting for about 63% of organic search traffic in the U.S., optimizing for mobile users is crucial. Use Google’s Lighthouse tool to test your site’s mobile-friendliness and implement necessary improvements.
13. Analyze Backlinks For More Targeted Outreach
Study your site’s backlink data to optimize your link-building strategy. Use this information to tailor your outreach strategy and target high-authority websites that are likely to find your content valuable.
14. Collaborate With Cross-Functional Teams
Communicate the value of SEO to all stakeholders and align it with broader business goals. Integrate feedback from various teams to improve your SEO workflow efficiency.
15. Monitor And Iterate
Remember, SEO isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it strategy. Continuously monitor your progress and be prepared to iterate based on new data and insights.
Tools To Find SEO Data
To implement these strategies effectively, you’ll need the right tools. Here are some essential ones:
- Google Analytics: For traffic data and user behavior insights. GA4 provides detailed information about your website visitors, including their demographics, interests, and how they interact with your site.
- Google Search Console: For keyword research and onsite data. Google Search Console shows you how your site appears in Google search results and can help you identify and fix indexing problems.
- Ahrefs: For backlink data and competitor analysis. It offers comprehensive insights into your backlink profile and helps you identify link-building opportunities.
- Semrush: For comprehensive competitor data and keyword research. It’s particularly useful for understanding your competitors’ strategies and finding keyword gaps.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: For technical SEO data. This tool crawls your website to identify technical issues that could be impacting your search engine performance.
- PageSpeed Insights: For Core Web Vitals analysis. It provides both lab and field data about page performance, with suggestions for improvement.
- Lighthouse: For mobile usability testing. This open-source tool audits performance, accessibility, progressive web apps, and more.
Remember, while these tools provide valuable data, the real power lies in how you interpret and act on this information.
Regularly review your data, look for trends and patterns, and use these insights to continuously refine your SEO strategy.
Leverage Data For Decision Making
Success in SEO isn’t luck or magic. With the right data, you can make informed strategies that cut through the noise and achieve better results on the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Remember, SEO is not just about theory – it’s about implementation. The final step of your data-driven decisions is to put your strategies into action and benchmark against your previous performance.
By leveraging data as a foundation for decision-making, you can create more effective SEO strategies.
From capitalizing on high-performing keywords to enhancing mobile usability and optimizing backlink strategies, each data-driven action you take helps solidify your online presence and improve your rankings.
Stay analytical, stay informed, and let the data illuminate your path to SEO success.
More resources:
- 7 Common Mistakes New Independent SEO Consultants Make (And How To Avoid Them)
- 15 Project Management Tools For SEO Professionals
- State Of SEO 2025
Featured Image: Deemerwha studio/Shutterstock
Extending Your Schema Markup From Rich Results To A Knowledge Graph
Harness the potential of Schema Markup to create a content knowledge graph that enhances search engine understanding of your web content.
 Martha van Berkel
10K Reads
Martha van Berkel
10K Reads
You probably know Schema Markup for its ability to help pages achieve a rich result. But did you also know that you can use Schema Markup to build a reusable content knowledge graph for your organization’s web content?
When SEO professionals do Schema Markup with the sole intention of achieving a rich result, they miss the opportunity to create semantic Schema Markup and build their content knowledge graph.
Content knowledge graphs enable search engines to contextualize the content on your site and make inferences more easily.
Let me illustrate the power of Schema Markup for inferencing by introducing myself. My name is Martha van Berkel, and this is my knowledge graph. It explains who I am and how I relate to other things.
- I studied at MIT and have a degree in Mathematics and Engineering.
- I am Canadian, the co-founder and CEO of Schema App, and I know a lot about Schema Markup.
- I worked at Cisco for 14 years.
- I also used to own a 1965 Austin Healey Sprite, and my car was in the movie “Losing Chase,” which Kevin Bacon directed. In fact, Kevin Bacon used to drive my car.
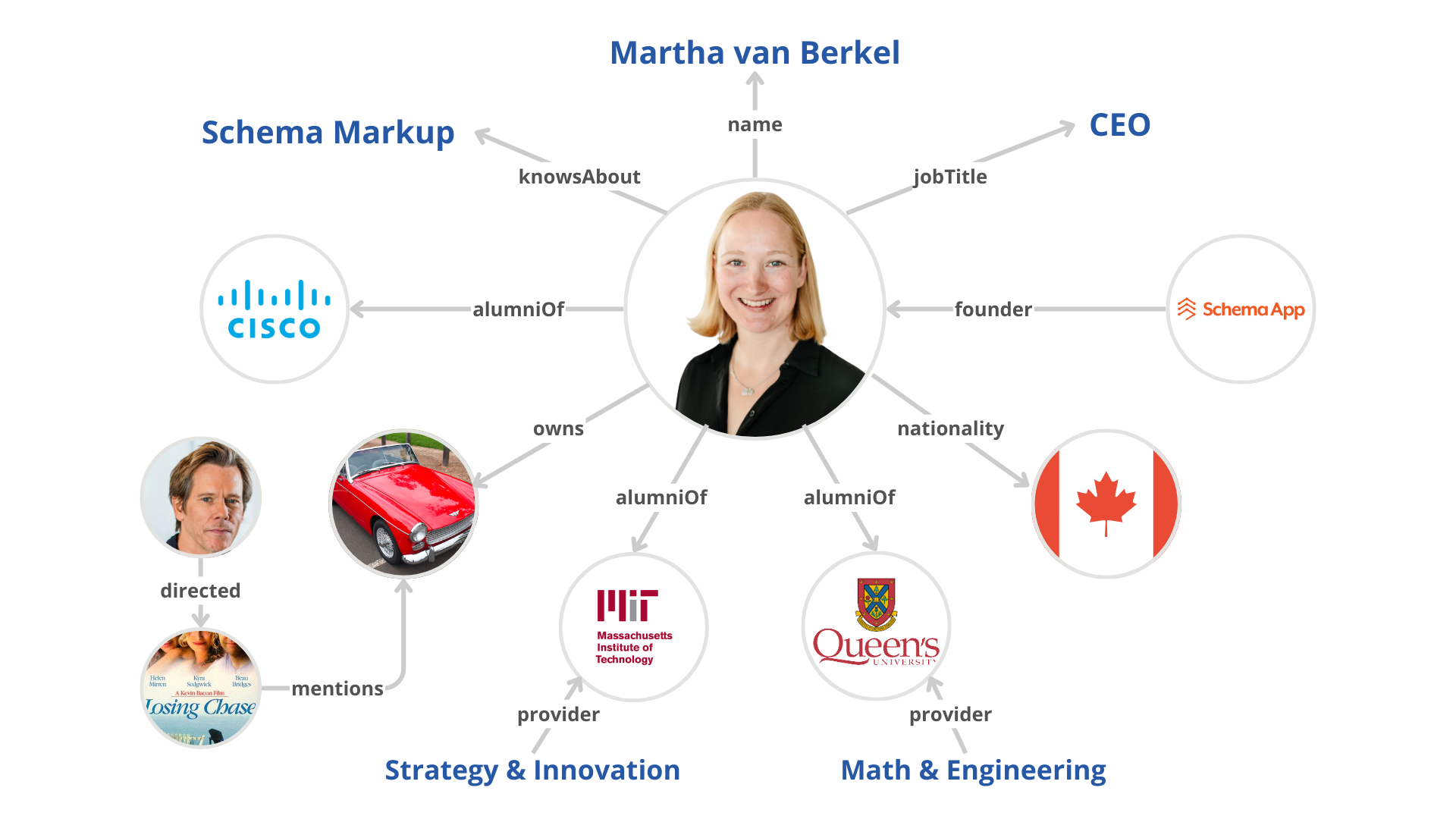 Image created by author, March 2024
Image created by author, March 2024
What can you infer from my knowledge graph? Are you thinking about how you can win the “6 degrees of separation from Kevin Bacon” game? Or are you thinking about how it makes sense that I know about Schema Markup and am writing about it because I am the CEO of Schema App?
You can make these inferences because of the understanding you’ve developed from reading the specific relationships within my knowledge graph. I used the properties for a Person Schema.org type to describe and define my relationship with these things, the same language we use to optimize our web pages.
If I didn’t specifically define the relationship between me and these other things, you might think that I work at Cisco, am a user of Schema App, and am related to Kevin Bacon. This is why being specific and adding context is important!
So, just like I used Schema Markup to bring context and clarity to who I am, you can use Schema Markup to add more context to your website content so that search engines and AI can make accurate, powerful inferences about it.
In this article, we will discuss why it is important to start thinking about Schema Markup for its semantic value and how you can use your Schema Markup to build a reusable content knowledge graph.
Why Is It Important To Start Thinking About Schema Markup For Its Semantic Value?
The search landscape is evolving quickly. Search engines are racing to provide a new search experience that leverages inferencing and chat experiences.
We see this in Google’s Gemini and Bing’s ChatGPT and from new entrants, such as Perplexity AI. In the chat experience, search engines need to be able to provide users with quick, accurate answers and deal with evolving contexts.
Consumers are now also using more hyper-longtail queries in their searches. Instead of searching for [female doctor Nashville women’s health], they are searching for [find me a female doctor who can help me with my cramps and has an appointment available within the next 2 days].
Search engines and large language models (LLMs) cannot easily infer the answer to this query across a company’s website data without understanding how the information is connected. This contextual inference is why search engines have moved from lexical to semantic search.
So, how do you make it easy for these machines to understand and infer things from your content? By translating your web content into a standardized vocabulary understood by humans and search engines – Schema Markup.
When you implement Schema Markup, you can identify and describe the things, also known as entities, on your site and use the schema.org properties to explain how they are related.
Entities are unique, well-defined, and distinguishable things or concepts. An entity can be a person, a place, or even a concept, and it has attributes and characteristics.
Your website content discusses entities related to your organization (e.g., brand, products, services, people, locations, etc.), and you can use Schema Markup to describe your entities and connect them with other entities on your site.
Entities are the foundational building blocks of a content knowledge graph.
The value of a content knowledge graph far exceeds SEO. Gartner’s 2024 Emerging Tech Impact Radar report identified knowledge graphs as a key software enabler and important investment to enable generative AI adoption.
Many AI projects are powered by large language models prone to hallucination and errors. Research shows that when paired together, knowledge graphs can provide factual knowledge, resulting in more accurate answers from the LLM.
By creating a content knowledge graph through Schema Markup, SEO pros can enable search engine understanding and help prepare their organization to be leaders in innovations with AI.
Read More: Entities & Ontologies: The Future Of SEO?
Implementing Schema Markup To Build A Content Knowledge Graph Vs. Just Rich Results
You might wonder: How is this different from implementing Schema Markup to achieve a rich result?
When an SEO pro’s goal is to achieve a rich result, they tend to only add Schema Markup to the pages and content that are eligible for the rich results. As such, they are only telling search engines small parts of the organization’s story.
They are not providing search engines with detailed information or context about the entities on their site and how they are connected to one another.
This leaves search engines to guess the intentions and meaning of their content – just like you might think I’m related to Kevin Bacon and work at Cisco if I didn’t establish my relationship with these things in my introduction.
When an SEO pro’s goal is to build a content knowledge graph, they use Schema Markup to identify, describe, and explain the relationship between the entities on their site so that search engines can truly understand and contextualize the information on their organization’s website.
So, how do you start creating your Schema Markup with the intention of building a knowledge graph?
How To Implement Schema Markup To Build Your Content Knowledge Graph
1. Identify The Pages On Your Website That Describe Your Key Entities
Your website can contain thousands of entities (like specific products, individuals, services, locations, and more).
However, certain entities are important to your business goals and outcomes. This content is often what you need people and search engines to know about so that you can convert them into customers or inform them about your brand.
Common key entities often include your organization, services, products, people, and brand, but this ultimately depends on your business objectives.
For example, if you are a healthcare provider looking to establish a trusted reputation and drive appointment bookings through your website, your key entities could include your organization, medical facilities, physicians, and services offered.
Once you’ve identified which entities are important to your organization, you can find the page on your site that best represents them. Ideally, each page would define one entity and how it relates to other entities on the site.
2. Use The Schema.org Vocabulary To Describe The Entities
When you implement Schema Markup on a page, you are using the Schema.org vocabulary to make a series of statements that describe the entity. The Schema.org type categorizes the entity, while the Schema.org property describes the entity.
For example, a physician detail page might include information about the physician’s name, medical specialty, who they work for, the hospital or medical clinic they work at, the medical services they provide, and the geographical area they serve.
You can use Schema Markup to describe these aspects of the entity and express it as a graph with specific connections.
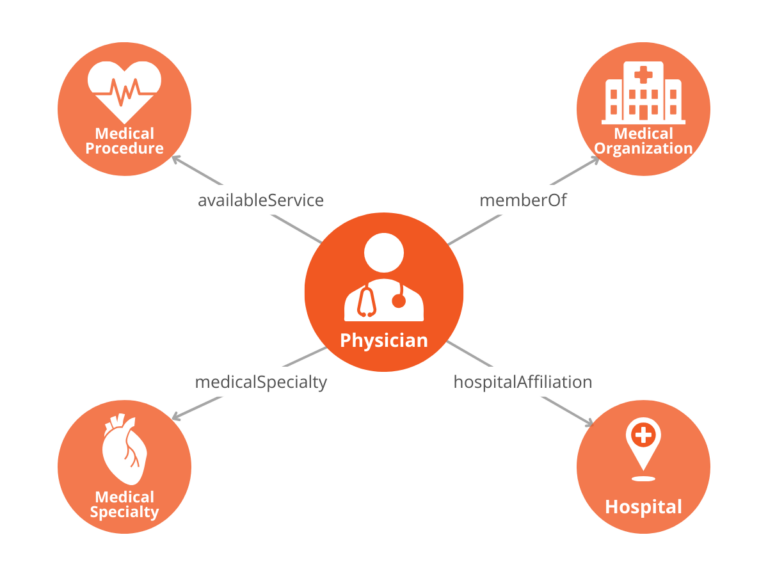 Image from author, March 2024
Image from author, March 2024
This helps search engines understand details about the physician to provide answers to a detailed query like [find me a cardiologist near me who can perform an EKG and has an appointment available in the next 2 days].
Every page on your website describes something about your business.
Implementing Schema Markup on each page clearly tells search engines what the page is about and how its concepts relate to other concepts on your website. Now, search engines and large language models can use this data to make inferences and confidently answer specific queries.
3. Connect The Entities On Your Website
Even though each web page is home to a unique entity, the content on your webpage might mention other entities that you’ve defined on other pages of your site.
If you want to build a content knowledge graph, you have to showcase how the entities on your website are connected and provide context using the right schema.org property.
This goes beyond a hyperlink connecting both pages using anchor text. With Schema Markup, you use the Schema.org properties that best describe the relationship to connect the entities.
For example, if the Physician works for the organization HealthNetwork, we can use the memberOf property to state that the Physician is a memberOf the Organization HealthNetwork.
 Image from author, March 2024
Image from author, March 2024
When you look at the content on the page, if there are URLs linked to take you to another step in the journey, these are entities that should be linked within the Schema Markup. For physicians, this may be the service line pages, the hospitals where they practice, etc.
This provides search engines with more contextual information about the physician, which enables them to answer more complex queries.
Using these basics, you have started building your content knowledge graph. This should be done in addition to trying to achieve rich results. However, the properties you use to connect your entities are likely different from Google’s required properties for the rich result.
4. Link Your Entities To Other External Authoritative Knowledge Bases To Disambiguate Them
In addition to connecting the entities on your site, you can further define the entities mentioned on your pages by linking them to known entities on external authoritative knowledge bases like Wikipedia, Wikidata, and Google’s Knowledge Graph.
This is known as entity linking.
Entity linking can help you define the entities mentioned in your text more explicitly so that search engines can disambiguate the entity identified on your site with greater confidence and showcase your page for more relevant queries.
At Schema App, we’ve tested how entity linking can impact SEO. We found that disambiguating entities like places resulted in pages performing better on [near me] and other location-based search queries.
Our experiments also showed that entity linking can help pages show up for more relevant non-branded search queries, increasing click-through rates to the pages.
Here’s an example of entity linking. If your page talks about “Paris”, it can be confusing to search engines because there are several cities in the world named Paris.
If you are talking about the city of Paris in Ontario, Canada, you can use the sameAs property to link the Paris entity on your site to the known Paris, Ontario entity on Wikipedia, Wikidata, and Google’s Knowledge Graph.
 Image from author, March 2024
Image from author, March 2024
Content Knowledge Graph Brings Context To Your Content
If your organization is using Schema Markup on select pages for the purpose of achieving a rich result, it is time to rethink your Schema Markup strategy.
Rich results can come and go.
However, the content knowledge graph you create using your Schema Markup can help search engines better understand and infer things about your organization through your content and prepare your organization to innovate with AI.
Like it or not, knowledge graphs are here to stay and you can start building yours by implementing proper semantic Schema Markup on your site.
More resources:
- Just How Important Is Structured Data In SEO?
- How To Maximize Your Reach Using Google’s Knowledge Graph
- Entities In SEO: What Are They And Why Do They Matter?
Featured Image: Gracia Chua/Schema App
Agile SEO: Moving From Strategy To Action
Achieve SEO success with agile methods. Learn how to get resources and buy-in from executives without lengthy strategy documents.
 Jes Scholz
13K Reads
Jes Scholz
13K Reads

Impactful SEO is rarely executed by a lone wolf.
You need resources. You need buy-in from higher-ups – a CMO, head of product, or even CEO.
But here’s the thing: those lengthy SEO documents outlining objectives, audiences, competitors, keywords, and that six-month Gantt chart vaguely detailing optimization projects – they’re not getting read.
On the contrary, it is a roadblock to you getting a green light for resources.
An executive can quickly scan one short email containing a clear request and sign off. However, they need to set aside dedicated time to read a strategy document in depth – and time is not something executives have a lot of.
And even if they sign off today, the reality is business priorities shift. Competitive landscapes change. Algorithms are updated.
SEO is executed in a constant state of flux. It demands flexibility on a monthly, even weekly basis.
So, let’s ditch the long documents and prioritize actions over proposals with agile SEO.
Why Agile SEO Strategies Work
Agile SEO involves incremental iteration.
Break complex, overarching projects down into small, frequent changes.
Enable continual progress.
 Image from author
Image from author
Forget the pursuit of SEO perfection.
The key is to launch a minimum viable product (MVP) and monitor the impact on metrics.
Once you are armed with performance data, you can move on. The key performance indicator (KPI) impact will get you buy-in for the resources you need.
Let me give you an example.
Say your overarching goal is to completely overhaul the website architecture of an e-commerce site – all the URL routes, page titles, meta descriptions, and H1s for the homepage, category pages, and product pages.
The Old Way: One Giant Leap
The traditional approach involves pitching the entire SEO project at once. Your argument is that it’s good for SEO.
The site will rank higher and significantly impact the organic sessions. Which is true.
However, the document communicating all the reasons and requirements is complicated to review.
The project will seem too large. It will likely not make it onto your development team’s roadmap, as they will likely feel your request will overload their development cycle.
 Image from author
Image from author
Agile SEO Approach: Small Iterations
What if you broke it down into micro-wins?
Instead of pitching the entire project, request approval for a small but impactful change.
For example, optimizing the title tag and meta description of the homepage.
The documentation for this will be less than one page. The change request is equivalent to snackable content. Because it’s easy to implement, it’s much easier to incorporate it into a development sprint.
Now, say this quick change positively impacts KPIs, such as a 3% lift in homepage organic sessions. You can then argue for similar changes for the category pages, pointing out that if we get a similar KPI lift as we did for the homepage, this will achieve X more organic sessions.
You have already proven such tactics can increase KPIs. So, there is more trust in your approach. And it’s, again, a small request. So, your development team is more likely to do it.
And you can rinse and repeat until you have the whole site migrated.
How To Document An Agile SEO Strategy
So now we know to stop writing long SEO strategy documents and instead start creating agile, “snackable” tactics.
But we still need to understand what:
- Has been completed in the past.
- Is being worked on now.
- Is coming up next.
- All the ideas are.
This information must be easy to digest, centrally accessible, and flexible.
One solution for this is an “SEO calendar” document.
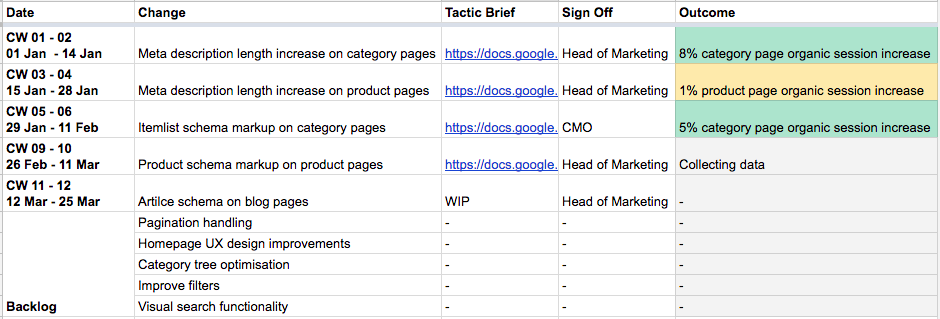
Elements of an SEO calendar:
- Date column: Ideally matched against IT sprint cycles. This does not mean every SEO initiative involves IT. But if you need a developer’s assistance, it will simplify cross-functional team projects. Having it set, for example, every two weeks also promotes small but constant releases from the SEO team.
- Backlog: This provides space for team members to record ideas without having to make any significant commitment of time. Assess all ideas regularly as you fill your next available calendar slot.
- Change column: A clear and concise sentence on what has been or will be changed.
- Tactic brief: A link to the detailed information of that test. More details coming below.
- Sign off: Ensuring all SEO changes pass a four-eye principle from a strategic point of view lowers the risk of any errors. These quick-to-read, snackable briefs make it easy to get your managers to buy in and sign off for resources.
- Outcome: One short sentence summing up the KPI impact.
The benefit of a calendar layout is it is fully flexible but time-relevant. Changing priorities is as simple as moving the de-prioritized item to the backlog.
It can act as a website change log for SEO. Everyone can know the timetable of changes, both past and planned upcoming.
Those interested in why the KPIs increased on a certain date have the answer at a glance and more detailed information in one click. This can be invaluable for troubleshooting.
And, for team leaders, if any gaps appear in the iteration cycle, you can see this as gaps will appear in the calendar, allowing you to address the root cause.
Snackable Tactic Briefs
The benefits of tactics briefs are twofold:
- Pre-launch: They concisely answer the Five Ws of your SEO change to get buy-in from stakeholders. Once aligned, it will act as the specification if you need someone else to execute it.
- Post-launch: Be the record of what was actually changed. What impact did it have on the KPI funnel? What did we learn? And what are the next steps, if any?
Tactics briefs have five sections:
- Overview.
- SMART Goal.
- Specifications.
- Results.
- Learnings & Action Items.
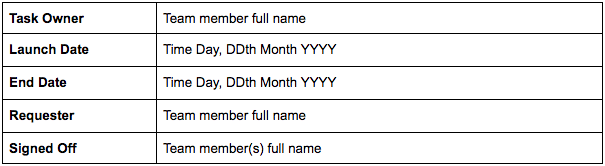
Overview
The overview section should cover the basics of the test:
- Who is the one person ultimately responsible for leading the execution of the test?
- When will it (pre-launch)/did it (post-launch) go live?
- When will we (pre-launch)/did we (post-launch) assess results?
- Who proposed the change? (It may be important to know if you need more information on the background for the test or if an action has come from senior management.)
- Who has agreed to this execution? (This may be development, the line manager in marketing, or another key stakeholder. Allowing everyone to see who is on board.)
 Screenshot from author
Screenshot from author
SMART Goal
The SMART goal is the high-level tactical approach.
Align your goal with your stakeholders before a detailed documentation effort goes into a task. This also ensures the change is in line with business goals.
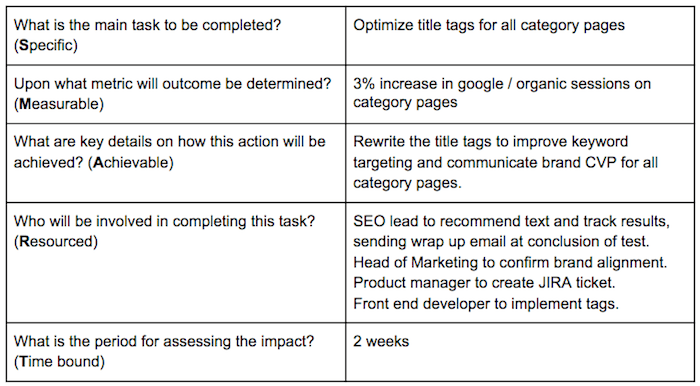
Specifications
This section will vary based on your test. But always try to communicate the “before” and the “after.” This way, you have a clear historical record you can refer back to.
The key is to have only the details needed. Nothing more, nothing less.
You can use tables to keep it easy to scan.
For example, in the case of a title tag change, it could be as simple as a single table.
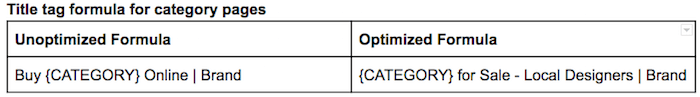 Screenshot from author
Screenshot from author
The key is to avoid long paragraphs of text. Focus on clearly communicating the outcome. What was it before, and what will be it after?
Don’t explain how the task was executed.
Results
This section should contain one table to effectively communicate the percentage change between the benchmark weeks and the SEO change from a full-funnel perspective, as well as any additional tables to drill down for more insights.
An example of a table could be similar to the one below.
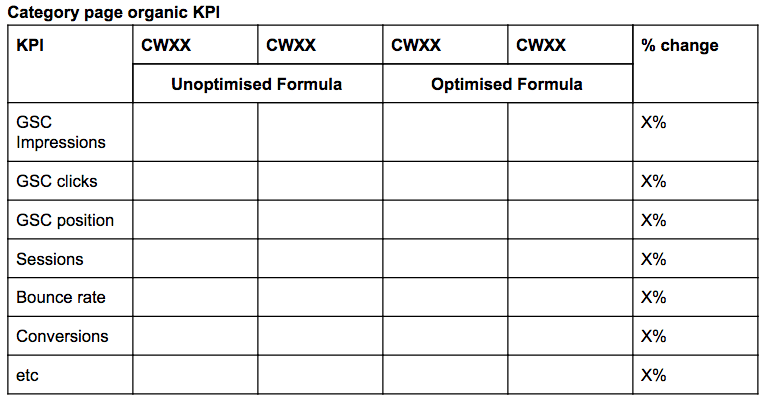 Screenshot from author
Screenshot from author
Learnings & Action Items
Here is where you can succinctly analyze the results.
Remember, you have the data clearly available in the table above, so you don’t need to list the numbers again.
Explain what the numbers mean and what actions will be taken next.
Final Thoughts
An agile SEO system provides flexibility and visibility.
At any time, you can understand what actions are underway and what has shifted KPIs.
Forget the fantasy of the perfect SEO strategy, and focus your energy on getting sh!t done.
More resources:
- Agile Budgeting: What It Is, Why It’s Impactful, And How To Make It Work For You As A Marketer
- 8 Ways To End Silo Mentality & Increase Business Agility
- SEO Trends 2024
Featured Image: Andrey_Popov/Shutterstock

 3 weeks ago
2
3 weeks ago
2




















 English (US) ·
English (US) ·